Configuration Overview
SD-Core has been developed with a cloud-based deployment and consumption model as its foundation. It has a rich and extensible set of APIs to allow for runtime configurability of subscriber management, access management, session management, and network slice management. This configuration may be conducted via ONF’s Runtime Operational Control (ROC) platform directly for consumption as a cloud-managed service, or the APIs can be used by third-party automation and management platforms.
Reference helm chart
Sub components in sdcore-helm-charts
omec-control-plane: 4G Network functions helm charts
5g-control-plane: 5G Network functions helm charts
omec-sub-provision: Simapp helm charts
5g-ran-sim : gNBSim helm charts
Configuration Methods
SD-Core supports 2 ways to configure network functions and micro services.
Helm Chart
Each individual network function and microservice has its own helm chart.
User needs to provide override values and deploy the network functions as per their need.
Use above helm charts appropriately and provide override values and install 4G/5G NFs.
REST Config Interface
Basic static configuration is still passed through helm chart ( logging level, image,…)
Dynamic Network Slice management APIs are provided through REST interface.
REST APIs are defined to create/modify/delete network slice.
REST APIs are also provided to provision subscribers and grouping the subscribers under device Group.
Note
Simapp is the example of REST interface based configuration to provision subscribers in SD-Core
Simapp is also used to provision Network Slices in SD-Core in the absence of Portal
Aether ROC Portal used REST interface to configure Network Slices in SD-Core
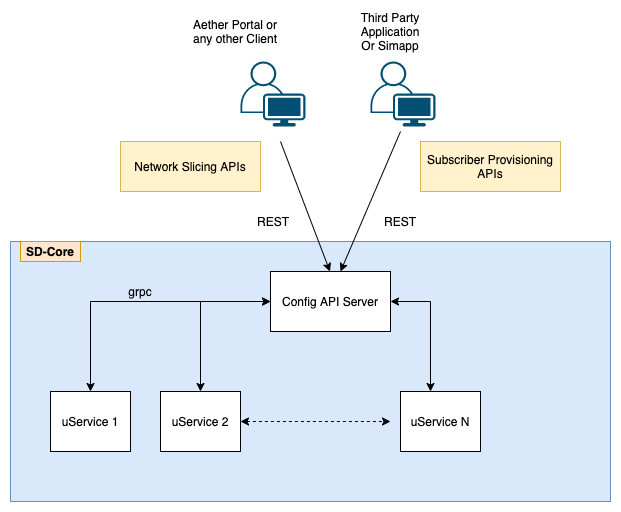
Configuration Steps
This Configuration describes what to configure at high level from RoC/SIMAPP. ConfigPod stores this configuration and publish to respective clients over REST/grpc.
Step1 : Provision subscriber in 4G/5G subsystem
Can be done only through SIMAPP
This step is used to configure IMSI in the SD-Core
This procedure is used to configure security keys for a subscriber
Subscribers can be created during system startup or later
Step2 : Device Group Configuration
Group multiple devices under device group
Configure QoS for the device group
Configure IP domain configuration for the device group e.g. MTU, IP Pool, DNS server
Step3: Network Slice Configuration
Configuration to create a Network Slice
Add device Group into Network Slice
Slice contains the Slice level QoS configuration
Site configuration including UPF, eNBs/gNBs assigned to the slice
Applications allowed to be accessed by this slice (see Application Filtering Overview)
Note
Step1 can only be done through Simapp. Look for simapp override values.
Step2 & Step3 can be done through Simapp or ROC. Simapp has option to create network slice. Look for configuration provision-network-slice: false in simapp configuration
Note
If UPF is used to allocate UE address allocation then even if you have specified UE address pool in the slice config, you still need to add the address pool configuration in the UPF deployment.
4G, 5G Configuration Differences
One of the most important difference in 4G & 5G configuration is around network slice. 5G has network slice Ids sent on 3gpp defined protocol messages whereas 4G does not have any slice Id in 3gpp defined protocol messages. We implement slicing in 4G using APNs. Let’s go over these difference in detail below,
Slice Id : Since 4G does not have slice Id in any protocol messages, configured slice Ids are ignored in 4G components. So it also means that even if configured slice Ids are duplicate it will not have any impact. But its still a good practice to have unique Slice Id per slice.
APN/DNN configuration: In case of 4G each slice should have separate APN. This is required because APN is used as slice identifier internally in the 4G modules. This is not true in case of 5G because 5G has slice Id along with APN/DNN. So in general its good practice to keep APN/DNN in the slice unique so same slice can work for 4G & 5G configuration.
DNN/APN in Initial Attach/Register Message : In case of 4G, if UE has set any random APN then MME overrides the APN based on the user profile in HSS. So its important to note that even if APN is not matching with configured APN we are still good. In case of 5G, apn name & Slice ID coming from UE is used to select SMF, so its important to have UE configured with correct APN/DNN name. Core network passed allowed slice IDs to UE in the registration accept message.